The Art and Science of Hair – Exploring Its Meaning and Significance
Published: 13 Oct 2024
Hair is more than just what grows from your scalp- it’s a powerful blend of biology, beauty, and identity. In this deep dive into The Art and Science of Hair: Exploring Its Meaning and Significance, we’ll uncover the secrets hidden within each strand. You’ll learn how hair is structured, what functions it serves, the different hair types, and why it matters more than we often realize. We’ll also explore how hair reflects health, culture, personality, and self-expression. Whether you’re curious about why your curls behave the way they do or you want to care for your hair the right way, this guide connects the science of hair with the art of loving and styling it. Ready to understand your hair like never before? Let’s begin.
The Importance of Hair
Hair has played a pivotal role in human societies throughout history. From ancient civilizations to modern cultures, hair has always been a symbol of beauty, status, and identity. Understanding what is hair reveals that its importance transcends mere aesthetics, influencing social norms and personal self-esteem.
In many cultures, hair signifies more than just appearance. For example, in ancient Egypt, both men and women adorned elaborate wigs, symbolizing their social status and fashion sense. In contemporary societies, hair continues to serve as an essential element of identity, with diverse hairstyles representing different cultural backgrounds and personal expressions.
Hair also impacts mental health. Research has shown that people experiencing hair loss often suffer from decreased self-esteem and increased anxiety. This highlights the emotional and psychological importance of hair, underscoring its role in our overall well-being.
The Structure of Hair
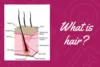
Understanding the anatomy of hair provides insights into its functions and care. Hair comprises three main layers: the cuticle, cortex, and medulla. Each layer plays a vital role in maintaining hair health and strength.
The Cuticle
The cuticle, the outermost layer, consists of overlapping cells that protect the inner layers from damage. A healthy cuticle ensures smooth, shiny hair, while a damaged cuticle can lead to frizz and breakage. Proper hair care routines, such as regular conditioning and gentle brushing, help maintain a healthy cuticle.
The Cortex
Beneath the cuticle lies the cortex, the thickest layer of the hair shaft. The cortex contains proteins and pigments that determine hair color and strength. Damage to the cortex can lead to weakened hair and loss of color vibrancy. Treatments such as protein masks and color-safe shampoos help protect and nourish the cortex.
The Medulla
The innermost layer, the medulla, is present in thicker hair types and provides additional structural support. While its function remains somewhat mysterious, it plays a role in the Secret to Thicker Hair by contributing to the overall integrity of the hair shaft.
Hair Growth Cycle
Hair growth follows a cyclic pattern, consisting of three phases: anagen, catagen, and telogen. Understanding these phases helps us better comprehend hair growth and loss.

Anagen Phase
The anagen phase, or growth phase, lasts from two to six years. During this period, hair follicles actively produce new hair cells, resulting in continuous hair growth. The length of the anagen phase determines the maximum length of one’s hair.
Catagen Phase
The catagen phase, or transition phase, lasts about two weeks. In this short period, hair growth stops, and the follicle begins to shrink. This phase marks the end of active hair production and the beginning of the hair’s detachment from the follicle.
Telogen Phase
The final phase, telogen, is the resting phase, lasting about three months. During this time, the hair remains in the follicle without growing. At the end of the telogen phase, the hair sheds, creating space for a new hair shaft to emerge from the follicle.
Common Hair Types
Hair types of hair vary significantly among individuals, influenced by factors such as genetics and ethnicity. Understanding different types of hair helps tailor hair care routines to meet specific needs.
Straight Hair
Straight hair, characterized by its smooth texture and lack of curls, tends to be more resilient to damage. However, it can become oily quickly due to the even distribution of natural scalp oils. Regular washing and lightweight products help manage straight hair.
Wavy Hair
Wavy hair, which falls between straight and curly, offers a natural, tousled look. This hair type can be prone to frizz and requires moisture-balancing products to maintain its natural wave pattern. Leave-in conditioners and anti-frizz serums are particularly beneficial for wavy hair.
Curly Hair
Curly hair, with its distinct ringlets, is often dry and prone to breakage. This hair type requires extra moisture and gentle handling to reduce damage. Deep conditioning treatments and protective hairstyles help maintain curly hair’s health and definition.
Hair Care Essentials
Proper hair care is crucial for maintaining healthy and beautiful hair. A consistent hair care routine tailored to individual hair types and needs makes a significant difference.
Washing
Regular washing keeps the scalp clean and free from excess oil and debris. However, over-washing can strip the hair of its natural oils, leading to dryness and damage. Finding the right balance is key, with most experts recommending washing two to three times a week.
Conditioning
Conditioning is vital for maintaining moisture and preventing tangles. Conditioners help smooth the hair cuticle, reducing frizz and enhancing shine. Deep conditioning treatments provide added hydration and can be incorporated weekly.
Heat Protection
Protecting hair from heat damage is critical for preserving its health. Heat styling tools, like flat irons and curling wands, can weaken the hair shaft and cause breakage. Using heat protectant sprays and limiting heat styling helps mitigate damage.
The Impact of Diet on Hair
A nutritious diet plays a crucial role in promoting healthy hair growth and preventing hair loss. One of the most effective hair growth tips is to fuel your body with vitamins, minerals, and proteins that support strong, vibrant hair.

Essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and proteins, contribute to hair strength and vitality.
Vitamins A and C
Vitamins A and C are vital for sebum production, which keeps the scalp moisturized. Foods rich in these vitamins, such as carrots, sweet potatoes, and citrus fruits, support healthy hair and scalp.
Protein
Protein is a fundamental building block of hair, and a lack of protein can lead to weak, brittle hair. Including protein-rich foods, such as lean meats, eggs, and legumes, strengthens hair and promotes growth.
Iron and Zinc
Iron and zinc are essential minerals that support hair follicle health. Iron-rich foods like spinach and lentils, along with zinc-rich sources like nuts and seeds, help prevent hair loss and promote healthy hair growth.
Hair Myths Debunked
Misconceptions about hair care can lead to ineffective practices and unnecessary concerns. Debunking common hair myths provides clarity and guides better hair care decisions.
Myth: Frequent Trims Accelerate Hair Growth
One prevalent myth is that cutting hair frequently leads to faster growth. While regular trims prevent split ends and maintain overall hair health, they do not affect the rate of hair growth. Hair growth occurs at the follicle level, unaffected by external trimming.
Myth: Brushing 100 Strokes Daily Enhances Shine
Another myth is that brushing hair 100 strokes per day promotes shine and growth. Over-brushing can cause breakage and damage, especially for delicate hair types. Instead, gentle brushing with a wide-toothed comb helps distribute natural oils and detangle hair without causing harm.
Myth: Daily Shampooing Is Necessary
The belief that daily shampooing is necessary for clean hair is also a misconception. Overwashing can strip the hair of its natural oils, leading
Conclusion
Hair is more than strands- it’s science, art, and identity. From its structure to its symbolism, hair reflects who we are and how we care for ourselves. Whether straight, wavy, curly, or coily, every hair type has unique needs. When you understand the art and science of hair, you can treat it better and love it more. Nourish it with the right foods, protect it from damage, and respect its natural form. With knowledge and care, healthy hair becomes not just a goal, but your everyday reality.
FAQs
The Art and Science of Hair” highlights the two sides of hair care and styling. The science involves understanding hair biology—its structure, growth cycle, and health. The art involves personal expression, cultural traditions, and creative styling choices. Together, they explain why hair is both a biological feature and a powerful symbol of beauty and identity.
Hair is often one of the first things people notice about each other. It reflects cultural background, personal style, and even social status in many societies. People use hair to express personality—whether through color, cuts, or styles. Because of this, hair plays a huge role in shaping self-image and confidence.
Hair is made of three main layers. The cuticle is the protective outer layer made of overlapping scales. The cortex is the middle layer that holds most of the hair’s strength, texture, and natural color. The medulla, the innermost layer, is sometimes absent in fine hair but helps with structure in thicker strands.
Hair grows in three main phases. The anagen phase is the active growth stage, lasting several years. The catagen phase is a short transitional stage where growth slows. The telogen phase is the resting stage, after which the hair sheds and new growth begins. Each strand is on its cycle, which is why we don’t lose all our hair at once.
Several factors influence how fast and healthy your hair grows. Diet plays a key role—nutrients like protein, iron, and vitamins A, C, and D are essential. Stress and hormonal imbalances can slow growth or trigger hair loss. Hair care habits, like avoiding harsh chemicals and heat, also impact overall growth and thickness.
Hair type is generally classified by curl pattern. Type 1 is straight, Type 2 is wavy, Type 3 is curly, and Type 4 is coily or kinky. Looking at your hair in its natural, dry state will give the clearest idea. Texture, density, and thickness also help define your exact type within these categories.
Trimming hair doesn’t actually change how fast your hair grows from the scalp. Growth happens internally, not at the ends. However, trimming split ends prevents breakage, making hair appear healthier and longer over time. So while it doesn’t speed up growth, it supports length retention and overall hair health.
Yes, washing hair daily can strip away natural oils that protect and moisturize your scalp and strands. This often leads to dryness, frizz, or even scalp irritation. Most people do best with washing two to three times per week. However, if your scalp is oily or you sweat a lot, gentle daily cleansing may work with a mild shampoo.
Unhealthy hair often looks and feels dry, brittle, or rough to the touch. Common signs include split ends, dullness, excessive tangling, and frequent breakage. If you notice more shedding than usual, it could also point to weakness or damage. Paying attention to these signs early helps you adjust your routine before damage worsens.
Healthy hair starts from the inside out, so eating a nutrient-rich diet and drinking enough water are crucial. Avoid overusing heat styling tools and harsh chemical treatments. Use gentle, sulfate-free products and deep-condition regularly to restore moisture. Protecting your hair at night with silk or satin can also improve long-term health.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks